IMPC Embryo Vignettes
The vignettes showcase the IMPC embryo pipeline. They highlight the different phenotyping procedures centres employ to phenotype embryonic lethal or subviable nulls. For more information on the pipeline refer to the: IMPC Embryo Pipeline Introduction, or read more in our paper High-throughput discovery of novel developmental phenotypes, Nature 2016. For a comprehensive list of lines with 3D image data refer to: IMPC 3D Embryo Data.
Chtoptm1a(EUCOMM)Wtsi
Chtop has been shown to recruit the histone-methylating methylosome to genomic regions
containing 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine, thus affecting gene expression.
Chtop mutants showed complete preweaning lethality with no homozygous pups observed.
High resolution episcopic microscopy (HREM) imaging at E14.5 revealed multiple
phenotypes including edema, abnormal forebrain morphology and decreased number of
vertebrae and ribs.
Phenotype data links
- Viability: Complete preweaning lethality
- 3-D imaging: Images
- Placental Histopathology: Images
- All adult and embryo phenotypes: Table
Klhdc2tm1b(EUCOMM)Hmgu
Kelch domain-containing protein 2 functions as a transcriptional corepressor through its inhibitory interaction with LZIP.
Klhdc2 mutants showed complete preweaning lethality with no homozygous pups observed, but remain viable up to E18.5. Micro-computed tomography (microCT) imaging revealed mutants display posterior polydactyly and edema. In addition to this, sections of microCT showed a smaller tongue, ventral septum defect (VSD), abnormal intestines and displaced kidneys.
The Kldhc2 gene is located within a locus linked to an automsomal dominant disease that
leads
to fibro-fatty replacement of right ventricle myocardium leading to arrythmias (ARVD3;
OMIM).
The gene is expressed in
heart
(expression atlas link) and has been implicated in endothelial
differentation and
myoblast
differentation.
Heterozygote null mice have abnormal heart rhythms while
the lethal embryos may have a heart defect.
Phenotype data links
- Viability: Adult Homozygous - Lethal, E12.5 Homozygous - Viable
- Embryo LacZ Expression: Images
- 3-D Imaging: 3D Viewer
- All adult and embryo phenotypes: Table
Acvr2atm1.1(KOMP)Vlcg
Activin receptor IIA is a receptor for activins, which are members of the TGF-beta
superfamily involved in diverse biological processes.
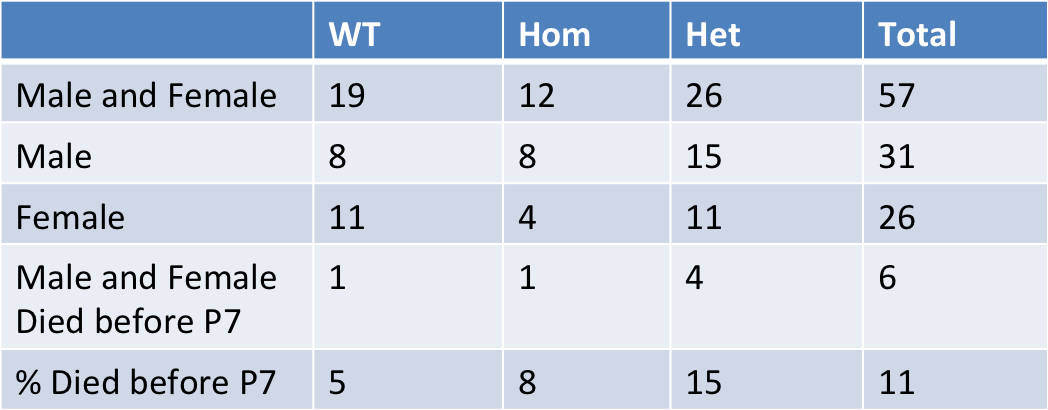
Acvr2a mutants are subviable with most pups dying before postnatal day 7. Micro-CT
analysis
at E15.5 revealed variable penetrance of eye and craniofacial abnormalities. Eye
phenotypes
varied from normal (Embryo 1- (E1)), to underdeveloped (E2), to cyclopic (E3), to absent
(E4). Craniofacial phenotypes varied from normal (E1) to narrow snout (E2), to an
elongated
snout missing the mandible and tongue (E3, 4) and low set ears (E2, 3, 4).
Phenotype data links
- Viability: Adult Homozygous - Subviable, E15.5 Homozygous - Viable
- Viability at P3/P7: Lethal
- Embryo LacZ Expression: Images
- Gross Morphology: E15.5 Images
- 3-D Imaging: 3D Viewer
- All adult and embryo phenotypes: Table
- Embryo Histopathology: Image
Cbx4tm1.1(KOMP)Vlcg
Chromobox 4 is in the polycomb protein family that are key regulators of transcription
and is reported to be upregulated in lung bud formation and required for thymus
development.
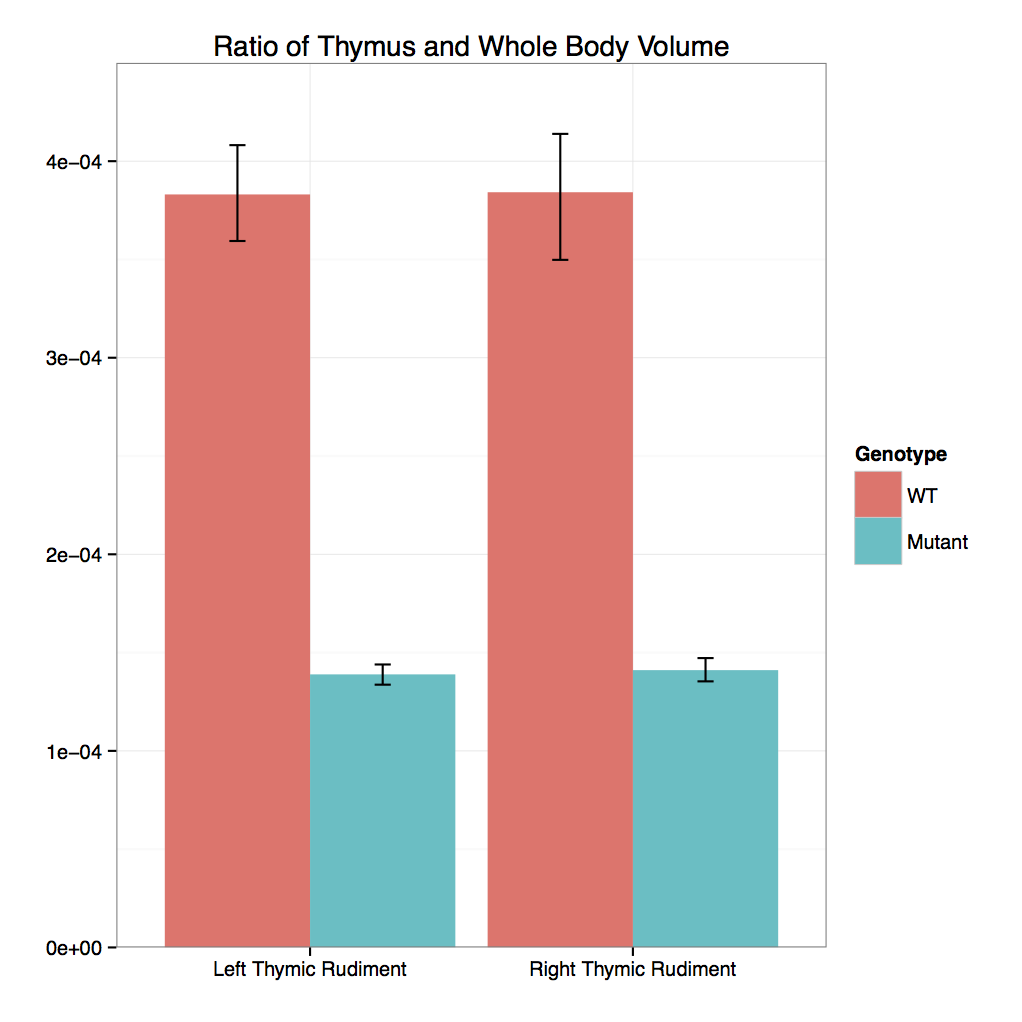
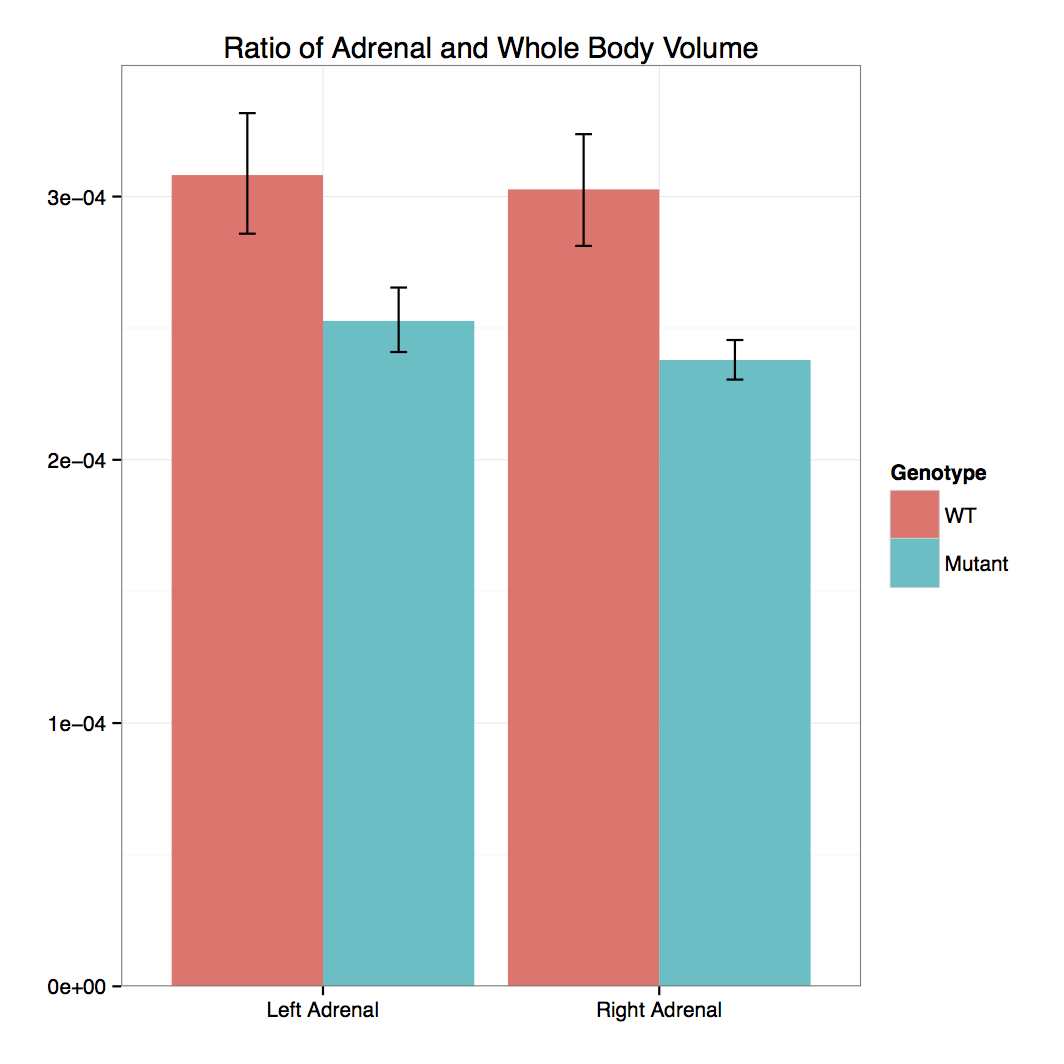
Cbx4 mutants showed complete preweaning lethality but were viable at E12.5 and E15.5
with no obvious gross morphological change.
Micro-CT analysis at E15.5 confirmed that
Cbx4tm1.1/tm1.1 mutants had statistically smaller
thymus and also revealed smaller adrenal glands and trigeminal ganglia compared to
Cbx4+/+ wildtype embryos.
Phenotype data links
- Viability: Adult Homozygous - Lethal, E12.5 Homozygous - Viable, E15.5 Homozygous - Viable
- 3-D Imaging: 3D Viewer
- All adult and embryo phenotypes: Table
- 3D Volumetric Analysis: Graph
 Automated MRI analysis of E15.5
Cbx4tm1.1/tm1.1 mutants viewed in coronal section
revealed that mutant embryos had bilateral smaller trigeminal ganglia, thymus, and adrenal
glands compared to
Cbx4+/+ wildtype embryos as indicated
by blue colour and highlighted by pink arrows (False Discovery Rate (FDR) threshold of 5%).
Automated MRI analysis of E15.5
Cbx4tm1.1/tm1.1 mutants viewed in coronal section
revealed that mutant embryos had bilateral smaller trigeminal ganglia, thymus, and adrenal
glands compared to
Cbx4+/+ wildtype embryos as indicated
by blue colour and highlighted by pink arrows (False Discovery Rate (FDR) threshold of 5%).
Tmem100tm1e.1(KOMP)Wtsi
Transmembrane Protein 100 functions downstream of the BMP/ALK1 signaling pathway.
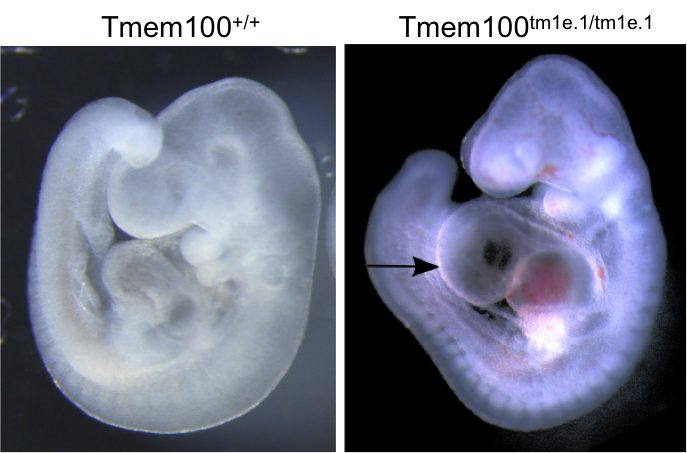
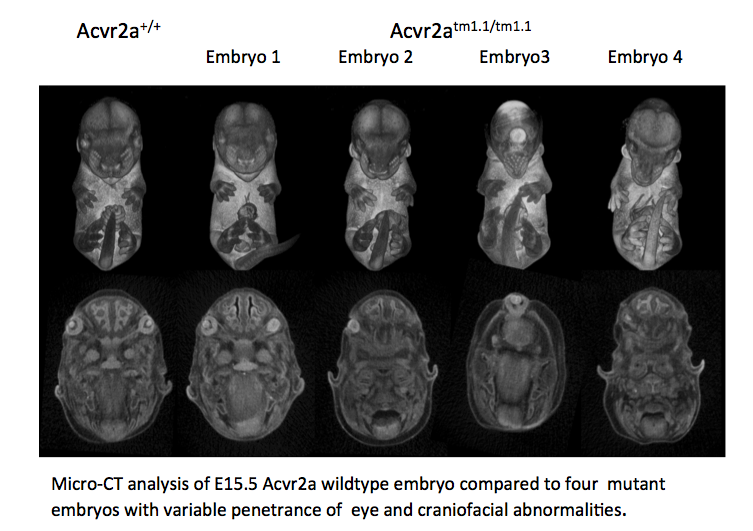
Tmem100 mutants showed complete preweaning lethality and were also lethal at E12.5.
LacZ staining in E12.5 Het embryos was found predominantly in arterial endothelial cells
and the heart (arrow) .
OPT analysis at E9.5 revealed that Tmem100 mutant embryos have a large pericardial
effusion with cardiac dysmorphology and enlargement (arrow).
Phenotype data links
- Viability: Adult Homozygous - Lethal, E9.5 Homozygous - Viable
- Gross Morphology: E9.5 Images
- 3-D Imaging: 3D Viewer
- All adult and embryo phenotypes: Table
 OPT analysis of E9.5 Tmem100
wildtype embryo compared to a
Tmem100tm1e.1/tm1e.1 mutant
embryo and lacZ staining in an E12.5
Tmem100+/tm1e.1
embryo.
OPT analysis of E9.5 Tmem100
wildtype embryo compared to a
Tmem100tm1e.1/tm1e.1 mutant
embryo and lacZ staining in an E12.5
Tmem100+/tm1e.1
embryo.
Eya4tm1b(KOMP)Wtsi
Eyes absent transcriptional coactivator and phosphatase 4 is associated with a variety
of developmental defects including hearing loss.
Eya4 mutants showed complete preweaning lethality with no homozygous pups observed.
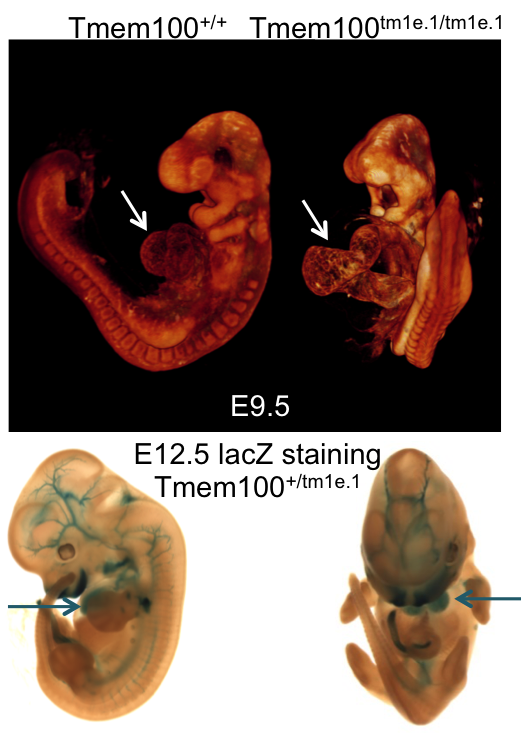
Micro-CT analysis at E15.5 revealed
Eyatm1b/tm1b
mutant embryos had bi-lateral smaller cochlear volumes as well as a smaller thyroid
gland, Meckel's cartilage, trachea (opening), cricoid cartilage, and arytenoid
cartilage.
Phenotype data links
- Viability: Adult Homozygous - Lethal, E12.5 Homozygous - Viable, E15.5 Homozygous - Viable
- Embryo LacZ Expression: Images
- Embryo Histopathology: Images
- 3-D Imaging: 3D Viewer
- All adult and embryo phenotypes: Table
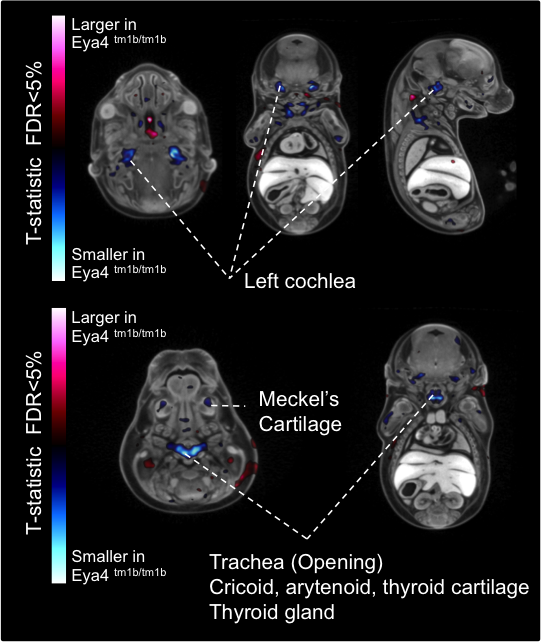 Automated MRI analysis of E15.5 Eya4tm1b/tm1b mutants showed that mutant embryos had a
statistically smaller
volumes of the cochlea and other tissues compared to
Eya4+/+ wildtype
embryos as highlighted in blue in transverse, coronal, and sagittal sections (false
discovery rate (FDR) threshold of 5%).
Automated MRI analysis of E15.5 Eya4tm1b/tm1b mutants showed that mutant embryos had a
statistically smaller
volumes of the cochlea and other tissues compared to
Eya4+/+ wildtype
embryos as highlighted in blue in transverse, coronal, and sagittal sections (false
discovery rate (FDR) threshold of 5%).
Tox3tm1b(KOMP)Mbp
Tox High Mobility Group Box Family Member 3 is a member of the HMG-box family involved in bending and unwinding DNA. Tox3 mutants have partial preweaning lethality with 1/3 of the pups dying before P7. Whole brain MRI at P7 revealed that Tox3tm1b/tm1b mutants had a much smaller cerebellum (blue) compared to the Tox3+/+ wildtype mice (as seen in coronal, sagittal, and axial section) and a relatively larger amygdala, thalamus, pons (red)
Phenotype data links- Viability: Adult Homozygous - Subviable
- Viability at P3/P7: Viable
- Embryo Histopathology: Images
- All adult and embryo phenotypes: Table
 Caudal to rostral coronal sections of whole brain MRI with automated volume analysis
revealed P7
Tox3tm1b/tm1b mutant mice had smaller (blue) and larger
(red) tissues compared
to the
Tox3+/+ wildtype average.
Caudal to rostral coronal sections of whole brain MRI with automated volume analysis
revealed P7
Tox3tm1b/tm1b mutant mice had smaller (blue) and larger
(red) tissues compared
to the
Tox3+/+ wildtype average.
Rsph9tm1.1(KOMP)Vlcg
Radial spoke head protein 9 is a component of the radial spoke head in motile cilia and flagella. Rsph9 mutants showed partial pre-weaning lethality but viable to P7. Whole brain MRI and H&E staining of coronal sections of the P7 brain revealed severe hydrocephaly of the left and right lateral ventricles of the Rsph9 mutant. Coronal section through the nasal region showed that the sinuses of the Rsph9 mutants were filled with pus (asterisks). Both hydrocephaly and nasal blockage are phenotypes associated with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia in humans.
Phenotype data links
- Viability: Adult Homozygous - Subviable
- Viability at P3/P7: Viable
- All adult and embryo phenotypes: Table
- Whole Brain MRI: Images
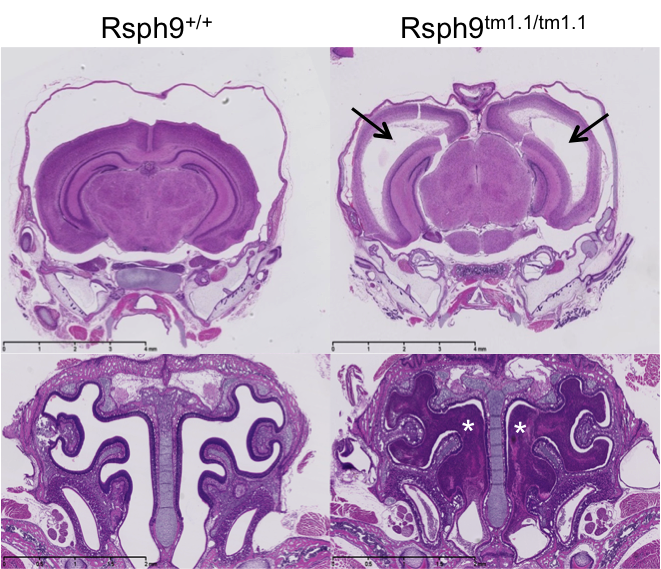 H&E stained coronal sections of P7 mice revealed enlarged ventricles and blocked sinuses
in the
Rsph9tm1.1/tm1.1 mutant mice.
H&E stained coronal sections of P7 mice revealed enlarged ventricles and blocked sinuses
in the
Rsph9tm1.1/tm1.1 mutant mice.
Pax7tm1.1(KOMP)Vlcg
Pax 7 is a nuclear transcription factor with DNA-binding activity via its paired
domain.
It is involved in specification of the neural crest and is an upstream regulator of
myogenesis during post-natal growth and muscle regeneration in the adult.
Pax7 mutants showed complete preweaning lethality.
Micro-CT analysis at E15.5 revealed voxel-wise local volume differences with a
larger nasal septum, cavity and capsule (False Discovery Rate <5%) in the E15.5
Pax7tm1.1/tm1.1 mutant embryos compared the
wildtype embryos.
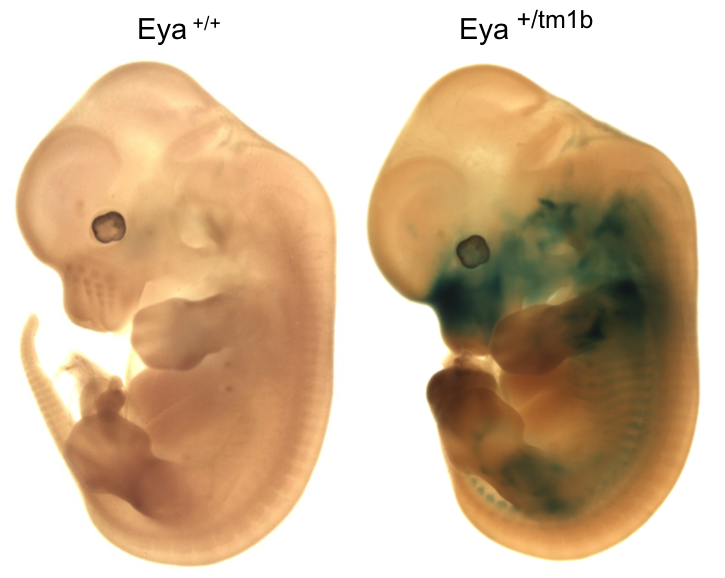
LacZ staining at E12.5 showed very strong staining in the medial region of the
frontonasal prominence (arrows) where structural changes were found.
LacZ staining was also seen in the midbrain, hindbrain, spinal cord, vertebrae, ribs
and neural crest.
Phenotype data links
- Viability: Adult Homozygous - Subviable
- Embryo LacZ Expression: Images
- 3-D Imaging: 3D Viewer
- All adult and embryo phenotypes: Table
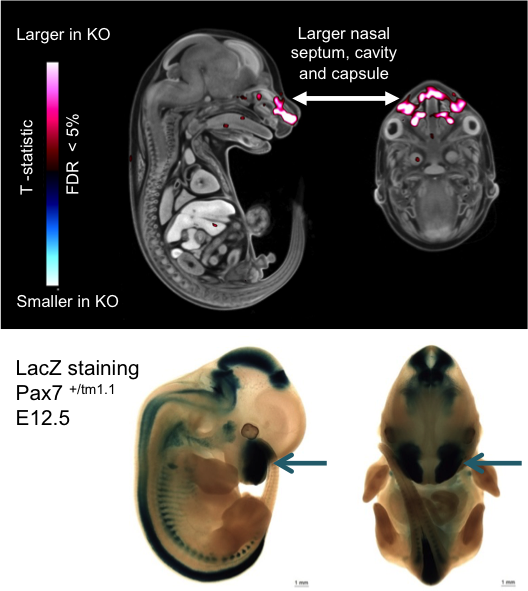 Micro-CT analysis of E15.5 Pax7 embryos and
lacZ staining of E12.5 embryos indicating volume changes and staining in the nasal area.
Micro-CT analysis of E15.5 Pax7 embryos and
lacZ staining of E12.5 embryos indicating volume changes and staining in the nasal area.
Svep1tm1b (EUCOMM)Hmgu/J
Svep1 codes for an uncharacterized protein named after the multiple domains identified in the sequence: Sushi, a domain common in adhesion and complement proteins; von Willebrand factor type A, occurring in extra-cellular matrix and integrin proteins; Epidermal Growth Factor, extra-cellular cysteine-rich repeats promoting protein-protein interactions; pentraxin domain containing 1, reactive with the complement system. No prior targeted mutations for this gene have been reported. Homozygous mutants show complete preweaning lethality, with embryonic lethality occurring after E18.5. Hemorrhaging is seen in surviving E18.5 mutants, as is severe edema and small embryo size (Fig 1, left). Among other defects, microCT analysis reveals brain defects, lung hypoplasia and absent renal pelvis in the kidney (Fig 1, middle, right). Phenotypes of heterozygotes include abnormal body composition and abnormal blood chemistry.
Phenotype data links
- Viability: Adult Homozygous - Lethal, E12.5 Homozygous - Subviable
- Embryo LacZ Expression: Images
- Gross Morphology: E18.5 Images, E15.5 Images
- 3-D Imaging: 3D Viewer
- All adult and embryo phenotypes: Table
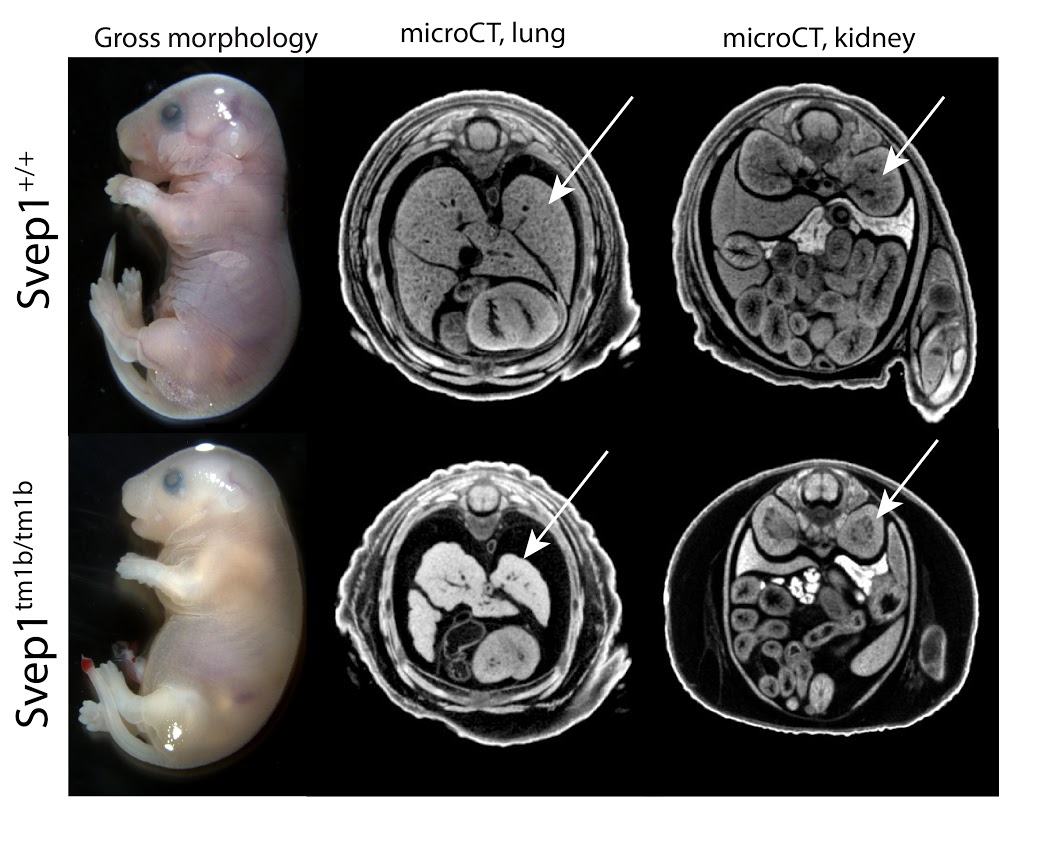
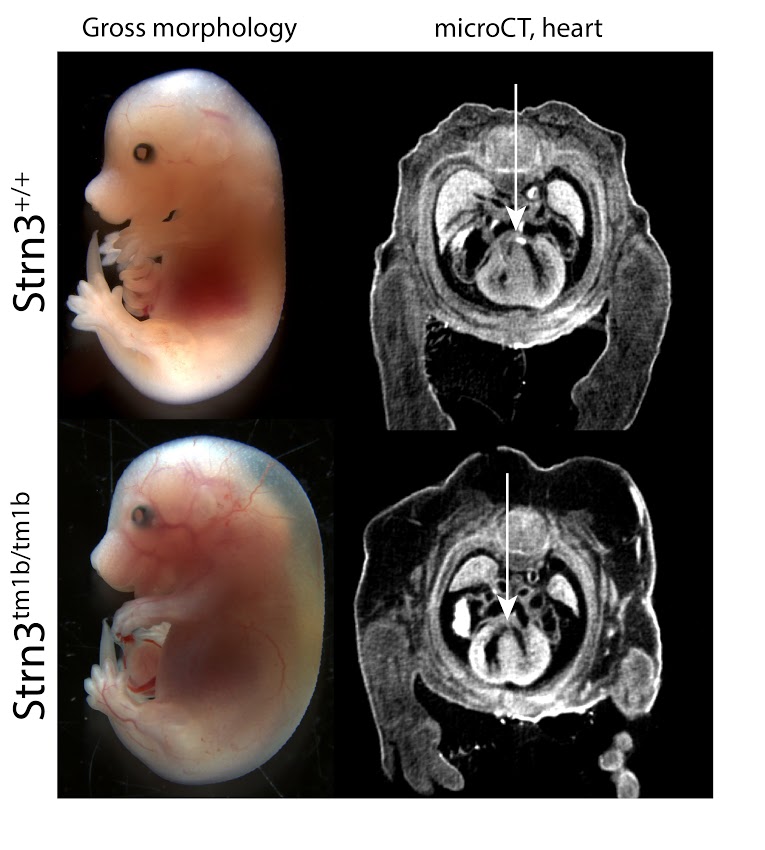
Strn3tm1b (KOMP)Wtsi/J
Striatins act as both calcium-dependent signaling proteins and scaffolding proteins, linking calcium-sensing signaling events with cellular action [1]. Strn3 homozygous mutants show complete preweaning lethality, with embryonic lethality occurring around E15.5. Surviving embryos are smaller in size and display both hemorrhaging and severe edema (Fig 1, left panels). MicroCT analyses reveal small, but consistent septal defects in heart (Fig 1, right panels). Multiple phenotypes are observed in heterozygous adult animals, including abnormal blood chemistry and hematology, impaired glucose tolerance and abnormal behavior, among others. A Genome-wide association study linking Strn3 with the canine disease Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy (ARVC) supports a role in cardiac function [2].
[1] The striatin family: a new signaling platform in dendritic spines, Benoist, M, et al, (2006) J. Physiol. Paris; [2] Identification of Striatin deletion in canine ARVC. (2010) Meurs, K. M., et al, Hum. Genet.
Phenotype data links
- Viability: Adult Homozygous - Lethal, E12.5 Homozygous - Viable,
- Embryo LacZ Expression: Images
- Gross Morphology: E15.5 Images
- 3-D Imaging: 3D Viewer
- All adult and embryo phenotypes: Table
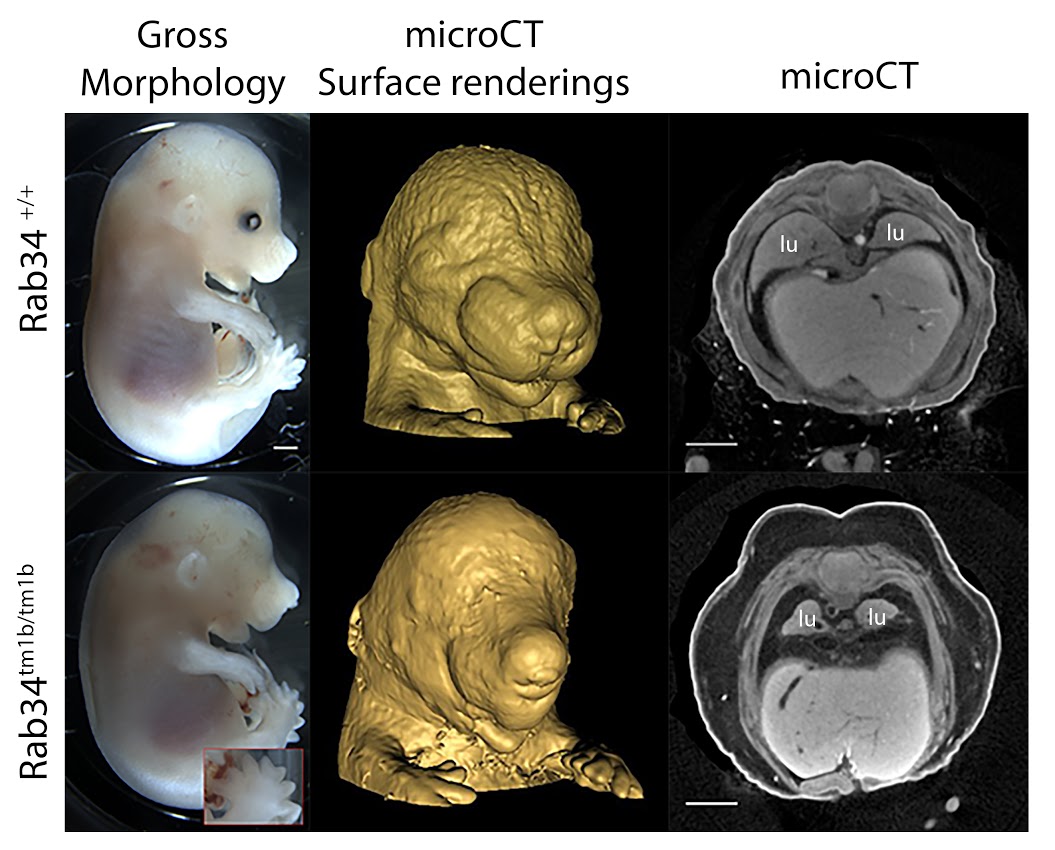
Rab34tm1b (EUCOMM)Hmgu/J
Rab34 is a member of the RAS oncogene family, which are small GTPases involved in intracellular vesicle transport. Rab34 is known to be Golgi-bound, involved in lysosomal positioning. Rab34 is a potential target of Gli1 and a possible component of hedgehog signaling. The Rab34 knockout is the first reported null allele for this gene, resulting in complete preweaning lethality. Phenotypes include patterning defects, such as polydactyly and facial clefting, as well as abnormal eye development and severe lung hypoplasia (Fig 1, lu = lung). The mutants are subviable at E18.5, lethality presumably occurring perinatally.
Phenotype data links
- Viability: Adult Homozygous - Lethal, E15.5 Homozygous - Viable
- Embryo LacZ Expression: Images
- Gross Morphology: E18.5 Images, E15.5 Images, E12.5 Images
- 3-D Imaging: 3D Viewer
- All adult and embryo phenotypes: Table
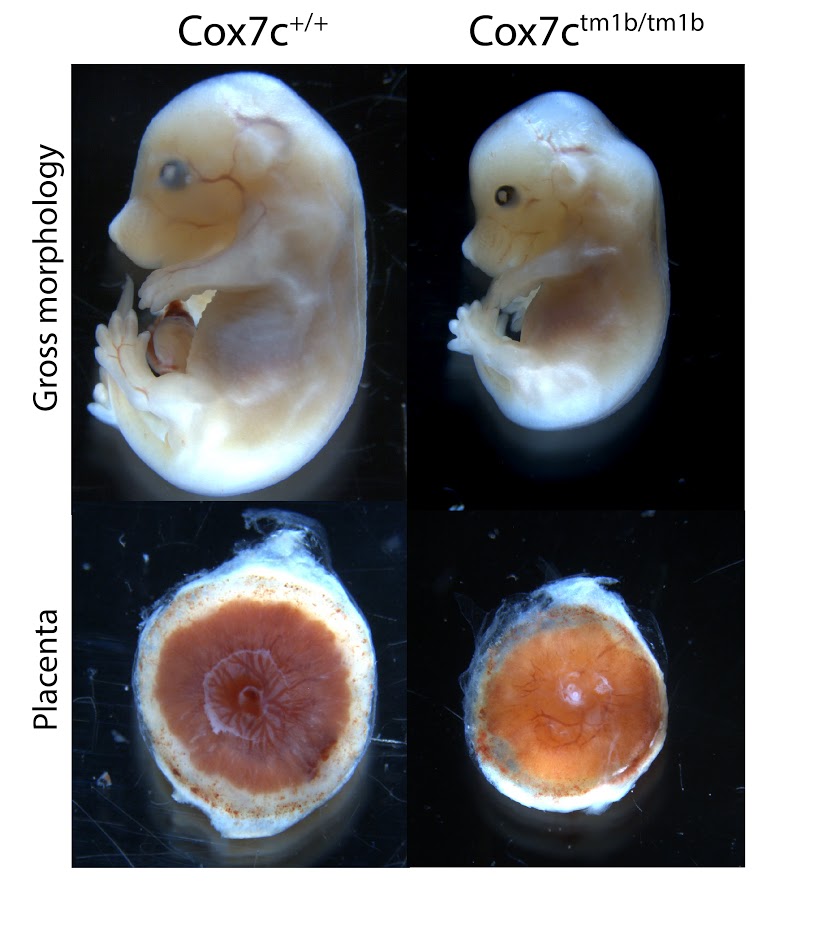
Cox7c tm1b (KOMP)Mbp
Cytochrome c oxidase subunit VIIc (Cox7c) is a nuclear-encoded regulatory component of cytochrome c oxidase. Homozygous mutants show complete preweaning lethality, with embryonic lethality occurring after E15.5. Surviving mutants are smaller (Figure 1, top panels), and have an abnormally small placenta (Figure 1, bottom panels). Although significant development progresses after E15.5, by E18.5 homozygous embryos die and begin to resorb.
Phenotype data links
- Viability: Adult Homozygous - Lethal
- Embryo LacZ Expression: Images
- Gross Morphology: E18.5 Images, E15.5 Images, E12.5 Images
- 3-D Imaging: 3D Viewer
- All adult and embryo phenotypes: Table
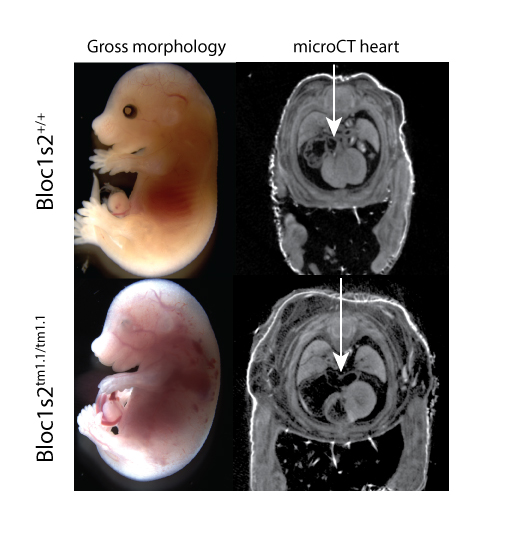
Bloc1s2tm1.1(KOMP)Mbp
Biogenesis of lysosomal organelles complex 1, subunit 2 is a component of the BLOC-1 complex, which functions in the formation of lysosome-related organelles, is implicated in synapse function, and is associated with gamma- tubulin and the centrosome [1]. Homozygous mutants show complete preweaning lethality, with embryonic lethality occurring around E15.5. Surviving mutants at E15.5 show edema, hemorrhage, and abnormal cardiovascular development (Fig 1). MicroCT datasets of E15.5 embryos also reveal lung hypoplasia, enlarged right atrium, and compromised right ventricle of the heart (Fig.1, arrow). Adult heterozygotes show abnormal immunophenotypes.
[1] Falcon-Perez et al., BLOC-1, a novel complex containing the pallidin and muted proteins involved in the biogenesis of melanosomes and platelet-dense granules, J Biol Chem 2002
Phenotype data links
- Viability: Adult Homozygous - Lethal
- Embryo LacZ Expression: No expression
- Gross Morphology: E12.5 Images
- 3-D Imaging: 3D Viewer
- All adult and embryo phenotypes: Table
Gfpt1tm1b(EUCOMM)Wtsi
Gfpt1 encodes glutamine:fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase 1, which catalyzes the transfer of an amino group from glutamine onto fructose-6-phosphate. This is the first and rate limiting enzyme of the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway.
Gfpt1 mutants showed complete lethality by E12.5 with no homozygous embryos observed. Optical projection tomography (OPT) at E9.5 illustrated developmental delay, craniofacial abnormalities, abnormal allantois development, failure to complete turning and abnormal heart looping.
Phenotype data links
- Viability: Adult Homozygous - Lethal, E12.5 Homozygous - Lethal
- Embryo LacZ Expression: Images
- 3-D Imaging: 3D Viewer
- All adult and embryo phenotypes: Table
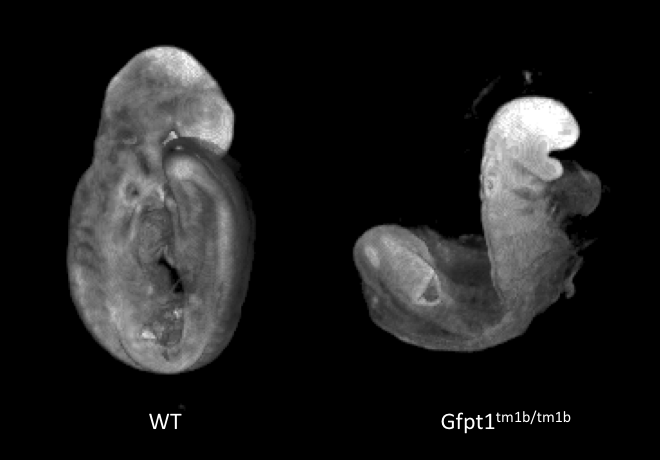 Developmental delay and failure to
turn in E9.5 Gfpt1-null mutants. Morphology captured by OPT.
Developmental delay and failure to
turn in E9.5 Gfpt1-null mutants. Morphology captured by OPT.
Atg3tm1b(EUCOMM)Hmgu
Atg3 is an E2-like protein-conjugating enzyme involved in autophagy broadly expressed during development and in the adult.
Atg3 mutants show complete preweaning lethality with no homozygous pups observed, but they are viable at least until E14.5. Micro-computed tomography (microCT) imaging at E14.5 revealed homozygous mutant fetuses had cardiovascular abnormalities such as ventral septum defects (VSD), thick atrio-ventricular valves and a thin myocardium, as well as an enlarged umbilical vein.
Phenotype data links
- Viability: Adult Homozygous - Lethal, E12.5 Homozygous - Viable, E14.5 Homozygous - Viable
- Embryo LacZ Expression: Images
- 3-D Imaging: 3D Viewer
- All adult and embryo phenotypes: Table
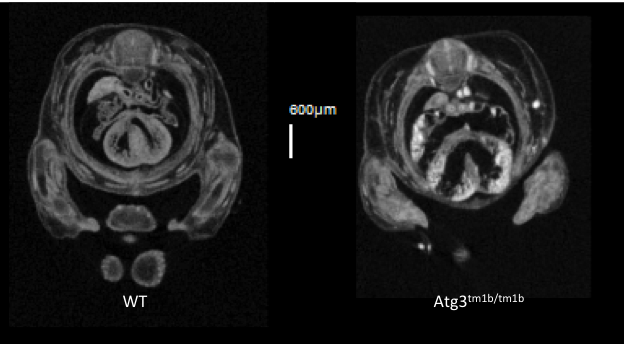 VSD seen in transverse section in
Atg3-null mutants.
VSD seen in transverse section in
Atg3-null mutants.
Kdm8tm1b(EUCOMM)Wtsi
Kdm8 encodes for lysine (K)-specific demethylase 8, which is predicted to have dual functions as a histone demethylase and as a protein hydroxylase. The gene is formerly known as Jmjd5.
Kdm8 tm1b homozygous mutants showed complete lethality by E12.5. Optical projection tomography (OPT) showed that at E9.5 mutant embryos appear small in size, remain unturned and that they are developmentally delayed by this stage of gestation. Interestingly. Kdm8 tm1a homozygous mutants can live up to the end of gestation, suggesting that the targeted trap is a hypomorphic allele.
Phenotype data links
- Viability: Adult Homozygous - Lethal
- Embryo LacZ Expression: Images
- 3-D Imaging: 3D Viewer
- All adult and embryo phenotypes: Table
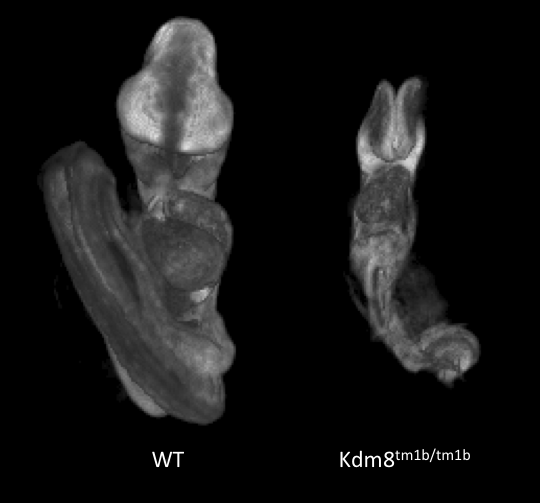 Developmental delay at E9.5 in
Kdm8tm1b/tm1b mutants.
Developmental delay at E9.5 in
Kdm8tm1b/tm1b mutants.
Slc39a8tm1b(EUCOMM)Wtsi
Solute carrier family 39 (metal ion transporter), member 8 encodes a protein that functions as a transporter for several divalent cations. Mutants show complete preweaning lethality with no homozygous pups observed, but are viable at least until E14.5. Micro-computed tomography (microCT) imaging at E14.5 revealed mutants were smaller and had cardiovascular abnormalities, such as ventral septum defects. It also revealed mutants lacked a sternum and had a small chest cavity and liver.
Phenotype data links
- Viability: Adult Homozygous - Lethal, E12.5 Homozygous - Viable
- Embryo LacZ Expression: Images
- 3-D Imaging: 3D Viewer
- All adult and embryo phenotypes: Table
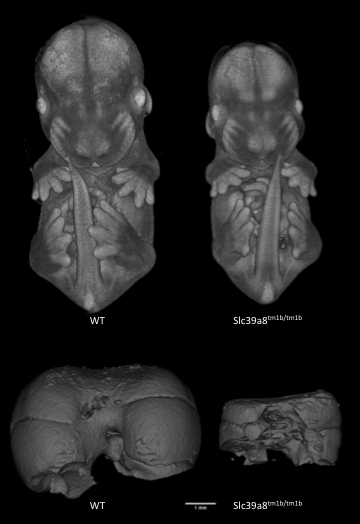
Slc39a8-null mutants are significantly smaller than WT littermates and have smaller livers.
Gygtm1b(KOMP)Wtsi
Glycogenin is an enzyme that converts glucose to glycogen. Glycogenin catalyzes UDP-alpha-D-glucose + glycogenin ⇌ UDP + alpha-D-glucosylglycogenin. The enzyme is a homodimer of 37 kDa subunits. Mutations in human GYG1 are associated with Glyocgen Storage Disease XV and Polyglucosan Body Myopathy 2 (OMIM). Homozygous null Gyg mice die between birth and weaning but were found in normal proportions at E18.5. Mutants were indistinguishable from littermates at E12.5, E15.5 or E18.5 but analysis of microCT images revealed obvious cardiac abnormalities, enlarged thymus and abnormal nervous system morphology. This is the first reported Gyg mouse mutant.
Phenotype data links
- Viability: Adult Homozygous - Lethal, E18.5 Homozygous - Viable
- Embryo LacZ Expression: Images
- 3-D Imaging: 3D Viewer
- All adult and embryo phenotypes: Table
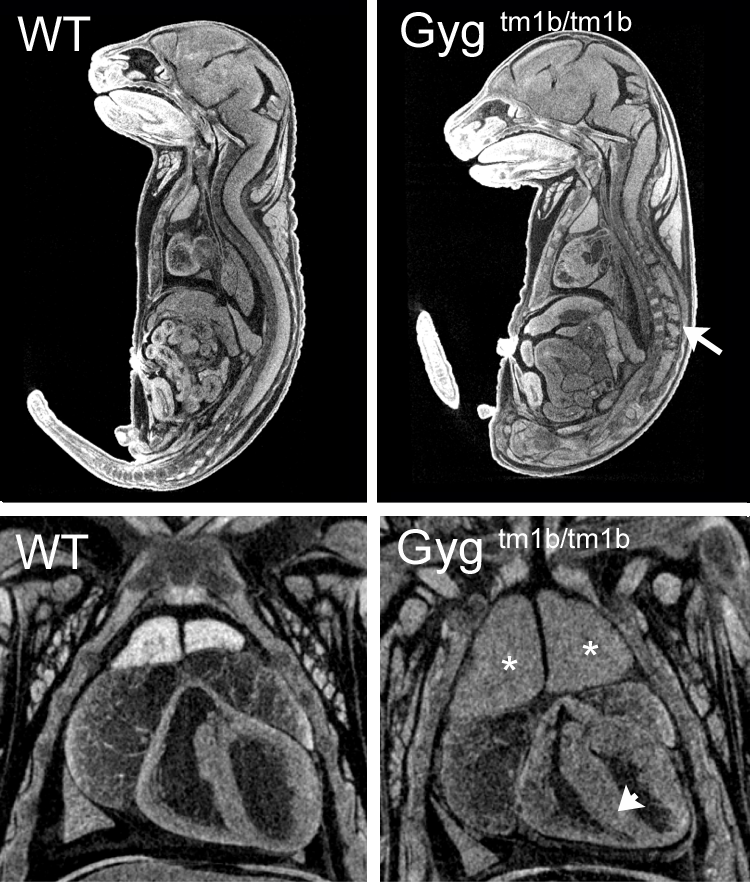
Single images from E18.5 microCT volumes showing spinal cord abnormalities (arrow), enlarged thymus (asterisk) and thickened myocardium (arrowhead) in homozygous null embryos compared to wild-type littermates.
Tmem132atm1b(KOMP)Wtsi
Transmembrane protein132a is transmembrane protein of unknown function. Homozygous null mutants were viable at normal proportions at E15.5 and E18.5 but showed obvious and severe defects that were readibly visible by eye. Embryos had abnormal limb morphology with syndactyly, spina bifida, heart abnormalities. Some mutants were smaller than littermates.
Phenotype data links
- Viability: Adult Homozygous - Lethal, E12.5 Homozygous - Viable, E18.5 Homozygous - Viable
- Embryo LacZ Expression: Images
- 3-D Imaging: 3D Viewer
- All adult and embryo phenotypes: Table
- Sagittal images from microCT: Centre provided image
- Axial images from microCT Centre provided image
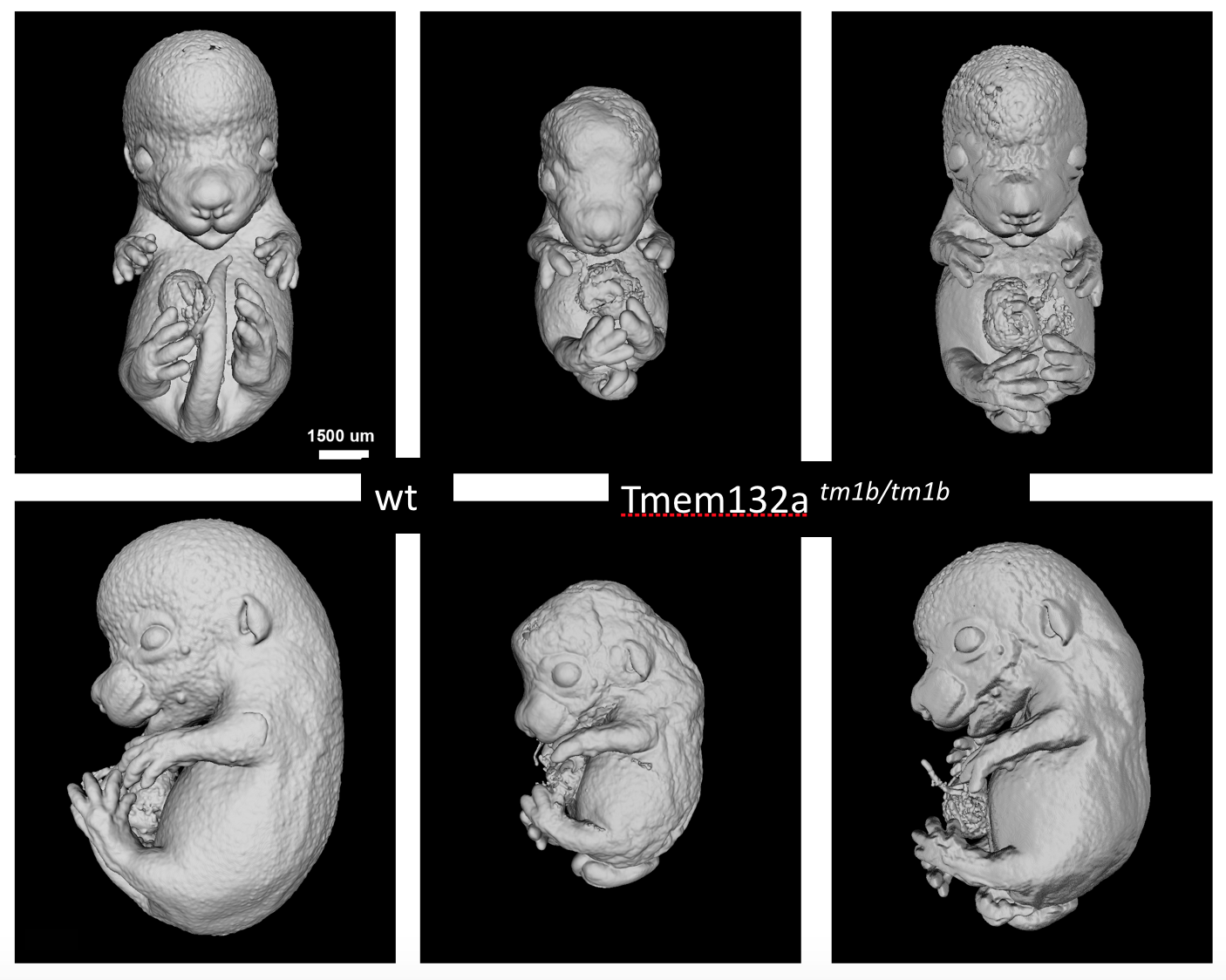
Surface renderings of microCT volumes of Tmem132a mutants compared to wildtype littermates


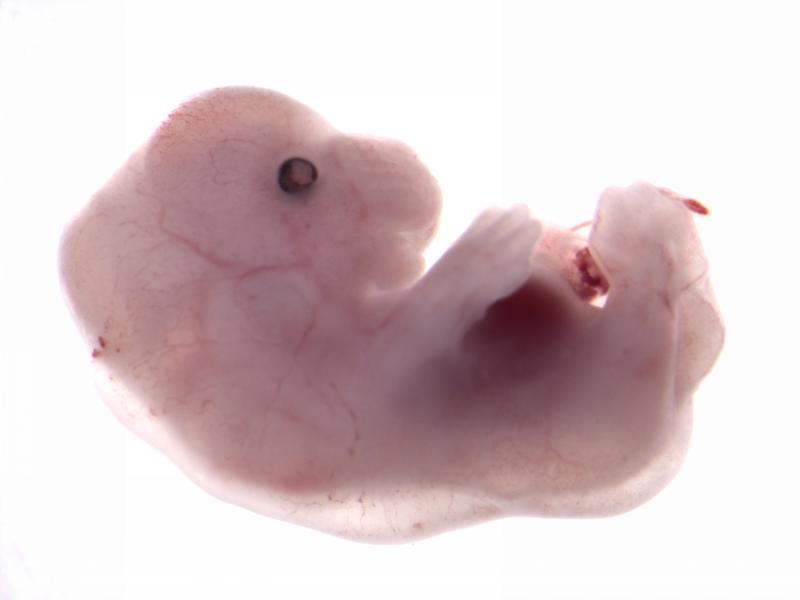 Chtop
null embryo
Chtop
null embryo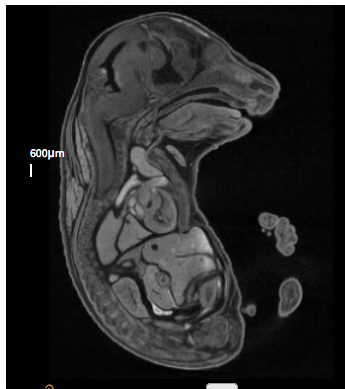 E18.5
Klhdc2 null embryo
E18.5
Klhdc2 null embryo